 Image credit: JoECP
Image credit: JoECP
Abstract
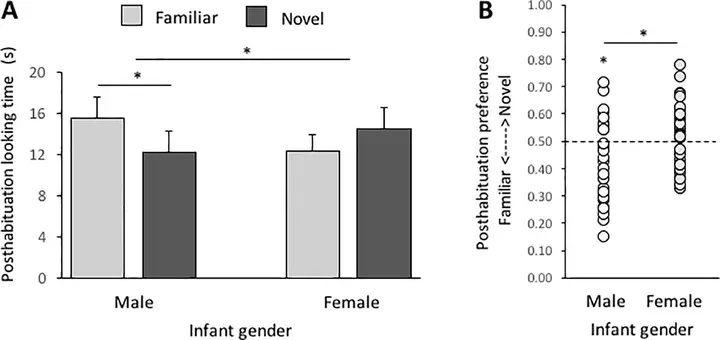
We examined mechanisms underlying infants’ ability to categorize human biological motion stimuli from sex-typed walk motions, focusing on how visual attention to dynamic information in point-light displays (PLDs) contributes to infants’ social category formation. We tested for categorization of PLDs produced by women and men by habituating infants to a series of female or male walk motions and then recording posthabituation preferences for new PLDs from the familiar or novel category (Experiment 1). We also tested for intrinsic preferences for female or male walk motions (Experiment 2). We found that infant boys were better able to categorize PLDs than were girls and that male PLDs were preferred overall. Neither of these effects was found to change with development across the observed age range (∼4–18 months). We conclude that infants’ categorization of walk motions in PLDs is constrained by intrinsic preferences for higher motion speeds and higher spans of motion and, relatedly, by differences in walk motions produced by men and women.
Supplementary notes can be added here, including code, math, and images.